Example Dysmalpy model generation, using wrapper
This notebook shows the user how to create a mock galaxy using the wrapper.
Includes the following components:
Disk + Bulge
NFW halo
Constant velocity dispersion
The structure of the notebook is the following:
Setup steps
Generate Dysmalpy 3D model cube
Running the model-generation wrapper
1) Setup steps
Import modules
from __future__ import (absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals)
import os
from dysmalpy.fitting_wrappers import dysmalpy_make_model, utils_io
from dysmalpy import plotting, fitting
INFO:numexpr.utils:Note: NumExpr detected 10 cores but "NUMEXPR_MAX_THREADS" not set, so enforcing safe limit of 8.
INFO:numexpr.utils:NumExpr defaulting to 8 threads.
Setup notebook
# Setup plotting
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
mpl.rcParams['figure.dpi']= 300
mpl.rc("savefig", dpi=300)
Set output path
Note this will override the
outdirspecified in the param file.(This is useful for the example here. When running from command line, it’s recommended to properly set the directories in the param file.)
# Where to save output files
outdir = '/Users/sedona/data/dysmalpy_test_examples/JUPYTER_OUTPUT_MODEL_WRAPPER/'
outdir = '/Users/jespejo/Dropbox/Postdoc/Data/dysmalpy_test_examples/JUPYTER_OUTPUT_MODEL_WRAPPER/'
# Load the parameters file from the examples directory
filepath = os.path.abspath(fitting.__file__)
param_path = os.sep.join(os.path.dirname(filepath).split(os.sep)[:-1]+["examples", "examples_param_files", "model_examples", ""])
param_filename = param_path+'make_model_3Dcube.params'
Settings in parameter file:
Note there are many commented out options / parameters. These given an more complete overview of the settings & parameters that can be specified with the fitting wrapper parameter files.
with open(param_filename, 'r') as f:
print(f.read())
# Example parameters file for fitting a single object with 1D data
# Note: DO NOT CHANGE THE NAMES IN THE 1ST COLUMN AND KEEP THE COMMAS!!
# See README for a description of each parameter and its available options.
# ******************************* OBJECT INFO **********************************
galID, GS4_43501 # Name of your object
z, 1.613 # Redshift
## GALAXY CENTER:
# IMPORTANT: 0 indexed, so coordinates go from [0, nX-1] and [0, nY-1].
# So if using QFitsView, will need to subtract 1 from both coords (as QFitsView goes from [1,nX] and [1,nY])
xcenter, None # Center position in cube, x coord. Default: (nX-1)/2.
ycenter, None # Center position in cube, y coord. Default: (nY-1)/2.
# ***************************** OUTPUT *****************************************
outdir, GS4_43501_3D_model_cube/ # Full path for output directory
# ***************************** OBSERVATION SETUP ******************************
# Instrument Setup
# ------------------
pixscale, 0.125 # Pixel scale in arcsec/pixel
fov_npix, 37 # Number of pixels on a side of model cube
spec_type, velocity # DON'T CHANGE!
spec_start, -1000. # Starting value for spectral axis // generally don't change
spec_step, 10. # Step size for spectral axis in km/s // generally don't change
nspec, 201 # Number of spectral steps // generally don't change
# LSF Setup
# ---------
use_lsf, True # True/False if using an LSF
sig_inst_res, 51.0 # Instrumental dispersion in km/s
# PSF Setup
# ---------
psf_type, Gaussian # Gaussian, Moffat, or DoubleGaussian
psf_fwhm, 0.55 # PSF FWHM in arcsecs
psf_beta, -99. # Beta parameter for a Moffat PSF
# ## ELLIPTICAL PSF:
# psf_type, Gaussian # Gaussian, Moffat, or DoubleGaussian
# psf_fwhm_major, 0.55 # PSF major axis FWHM in arcsecs
# psf_fwhm_minor, 0.25 # PSF minor axis FWHM in arcsecs
# psf_PA, 0. # PA of PSF major axis, in deg E of N. (0=N, 90=E)
# psf_beta, -99. # Beta parameter for a Moffat PSF
# # DoubleGaussian: settings instead of psf_fwhm
# psf_type, DoubleGaussian
# psf_fwhm1, 0.16 # FWHM of PSF component 1, in arcsecs. SINFONI AO: 0.16
# psf_fwhm2, 0.48 # FWHM of PSF component 1, in arcsecs. SINFONI AO: 0.48
# psf_scale1, 0.368 # Flux scaling (*not* peak height) of component 1. SINFONI AO: 0.368
# psf_scale2, 0.632 # Flux scaling (*not* peak height) of component 2. SINFONI AO: 0.632
# **************************** SETUP MODEL *************************************
# Model Settings
# -------------
# List of components to use: SEPARATE WITH SPACES
## MUST always keep: geometry zheight_gaus
## RECOMMENDED: always keep: disk+bulge const_disp_prof
components_list, disk+bulge const_disp_prof geometry zheight_gaus halo
# possible options:
# disk+bulge, sersic, blackhole
# const_disp_prof, geometry, zheight_gaus, halo,
# radial_flow, uniform_planar_radial_flow, uniform_bar_flow, uniform_wedge_flow,
# unresolved_outflow, biconical_outflow,
# CAUTION: azimuthal_planar_radial_flow, variable_bar_flow, spiral_flow
# List of components that emit light. SEPARATE WITH SPACES
## Current options: disk+bulge / bulge / disk [corresponding to the mass disk+bulge component],
## also: light_sersic, light_gaussian_ring
light_components_list, disk
# NOTE: if a separate light profile (eg light_sersic) is used,
# this MUST be changed to e.g., 'light_components_list, light_sersic'
adiabatic_contract, False # Apply adiabatic contraction?
pressure_support, True # Apply assymmetric drift correction?
noord_flat, True # Apply Noordermeer flattenning?
oversample, 3 # Spatial oversample factor
oversize, 1 # Oversize factor
zcalc_truncate, True # Truncate in zgal direction when calculating or not
n_wholepix_z_min, 3 # Minimum number of whole pixels in zgal dir, if zcalc_truncate=True
# ********************************************************************************
# DISK + BULGE
# ------------
# Initial Values
total_mass, 11.0 # Total mass of disk and bulge log(Msun)
bt, 0.3 # Bulge-to-Total Ratio
r_eff_disk, 5.0 # Effective radius of disk in kpc
n_disk, 1.0 # Sersic index for disk
invq_disk, 5.0 # disk scale length to zheight ratio for disk
n_bulge, 4.0 # Sersic index for bulge
invq_bulge, 1.0 # disk scale length to zheight ratio for bulge
r_eff_bulge, 1.0 # Effective radius of bulge in kpc
# # ********************************************************************************
# # BLACK HOLE
# # ------------
#
# # Initial Values
# BH_mass, 11. # log(Msun)
# # ********************************************************************************
# # Separate light profile: (Truncated) Sersic profile
# # ------------
# # Initial values
# L_tot_sersic, 1. # arbitrary units
# lr_eff, 4. # kpc
# lsersic_n, 1. # Sersic index of light profile
# lsersic_rinner, 0. # [kpc] Inner truncation radius of sersic profile. 0 = no truncation
# lsersic_router, inf # [kpc] Outer truncation radius of sersic profile. inf = no truncation
# # ********************************************************************************
# # Separate light profile: Gaussian ring
# # ------------
# # Initial values
# L_tot_gaus_ring, 1. # arbitrary units
# R_peak_gaus_ring, 6. # kpc
# FWHM_gaus_ring, 1. # kpc
# ********************************************************************************
# ********************************************************************************
# ********************************************************************************
# DARK MATTER HALO
# ----------------
# Halo type: options: NFW / twopowerhalo / burkert / einasto / dekelzhao
halo_profile_type, NFW
# ** NOTE **: Uncomment the section below corresponding to the selected halo type.
# ********************************************************************************
# NFW halo
# Initial Values
mvirial, 11.5 # Halo virial mass in log(Msun)
halo_conc, 5.0 # Halo concentration parameter
fdm, -99 # Dark matter fraction at r_eff_disk
# Tie the parameters?
fdm_tied, True # for NFW, fdm_tied=True determines fDM from Mvirial (+baryons)
# ********************************************************************************
# # ********************************************************************************
# # Two-power halo
#
# # Initial Values
# mvirial, 11.5 # Halo virial mass in log(Msun)
# halo_conc, 5.0 # Halo concentration parameter
# fdm, 0.5 # Dark matter fraction at r_eff_disk
# alpha, 1. # TPH: inner slope. NFW has alpha=1
# beta, 3. # TPH: outer slope. NFW has beta=3
#
# # Tie the parameters?
# fdm_tied, True # for non-NFW, fdm_tied=True determines fDM from other halo params (+baryons)
#
# # ********************************************************************************
# # ********************************************************************************
# # Burkert halo
#
# # Initial Values
# mvirial, 11.5 # Halo virial mass in log(Msun)
# halo_conc, 5.0 # Halo concentration parameter
# fdm, 0.5 # Dark matter fraction at r_eff_disk
# rB, 10. # Burkert: Halo core radius, in kpc
#
# # Tie the parameters?
# fdm_tied, True # for non-NFW, fdm_tied=True determines fDM from other halo params (+baryons)
#
# # ********************************************************************************
# # ********************************************************************************
# # Einasto halo
# # Initial Values
# mvirial, 11.5 # Halo virial mass in log(Msun)
# halo_conc, 5.0 # Halo concentration parameter
# fdm, 0.5 # Dark matter fraction at r_eff_disk
# alphaEinasto, 1. # Einasto: Halo profile index
#
# # Tie the parameters?
# fdm_tied, True # for non-NFW, fdm_tied=True determines fDM from other halo params (+baryons)
#
# # ********************************************************************************
# # ********************************************************************************
# # Dekel-Zhao halo
# # Initial Values
# mvirial, 12.0 # Halo virial mass in log(Msun)
# s1, 1.5 # Inner logarithmic slope (at resolution r1=0.01*Rvir)
# c2, 25.0 # Concentration parameter (defined relative to c, a)
# fdm, 0.5 # Dark matter fraction at r_eff_disk
#
# # Tie the parameters?
# fdm_tied, True # for non-NFW, fdm_tied=True determines fDM from other halo params (+baryons)
#
# # ********************************************************************************
# ********************************************************************************
# INTRINSIC DISPERSION PROFILE
# ----------------------------
# Initial Values
sigma0, 39.0 # Constant intrinsic dispersion value
# ********************************************************************************
# ********************************************************************************
# ********************************************************************************
# HIGHER ORDER COMPONENTS: INFLOW, OUTFLOW
# ----------------------------------------
# # ********************************************************************************
# # UNIFORM SPHERICAL RADIAL FLOW -- in rhat direction in spherical coordinates
# # radial_flow
# # -------------------
#
# vr, -90. # Radial flow [km/s]. Positive: Outflow. Negative: Inflow.
# # ********************************************************************************
# # UNIFORM PLANAR RADIAL FLOW -- in Rhat direction in cylindrical coordinates
# # (eg, radial in galaxy midplane)
# # uniform_planar_radial_flow
# # -------------------
#
# vr, -90. # Radial flow [km/s]. Positive: Outflow. Negative: Inflow.
# # ********************************************************************************
# # UNIFORM BAR FLOW -- in xhat direction along bar in cartesian coordinates,
# # with bar at an angle relative to galaxy major axis (blue)
# # uniform_bar_flow
# # -------------------
#
# vbar, -90. # Bar flow [km/s]. Positive: Outflow. Negative: Inflow.
# phi, 90. # Azimuthal angle of bar [degrees], counter-clockwise from blue major axis.
# # Default is 90 (eg, along galaxy minor axis)
# bar_width, 2 # Width of the bar perpendicular to bar direction.
# # Bar velocity only is nonzero between -bar_width/2 < ygal < bar_width/2.
# # ********************************************************************************
# # UNIFORM WEDGE FLOW -- in planar radial flow in cylindrical coordinates, restricted to pos, neg wedges
# # uniform_wedge_flow
# # -------------------
#
# vr, -90. # Radial flow [km/s]. Positive: Outflow. Negative: Inflow.
# theta, 60. # Opening angle of wedge [deg]. (the full angular span)
# phi, 90. # Angle offset relative to the galaxy angle, so the wedge center is at phi.
# # Default: 90 deg, so centered along minor axis
# # ********************************************************************************
# # UNRESOLVED OUTFLOW -- at galaxy center (ie, AGN unresolved outflow)
# # unresolved_outflow
# # -------------------
#
# vcenter, 0. # Central velocity of the Gaussian in km/s
# fwhm, 1000. # FWHM of the Gaussian in km/s
# amplitude, 1.e12 # Amplitude of the Gaussian, for flux in ~M/L=1 luminosity units
# # with the dimming applied ... roughly ....
# # ********************************************************************************
# # BICONICAL OUTFLOW
# # biconical_outflow
# # -------------------
#
# n, 0.5 # Power law index
# vmax, 500. # Maximum velocity of the outflow in km/s
# rturn, 5. # Turn-over radius in kpc of the velocty profile
# thetain, 30. # Half inner opening angle in degrees. Measured from the bicone axis
# dtheta, 20. # Difference between inner and outer opening angle in degrees
# rend, 10. # Maximum radius of the outflow in kpc
# norm_flux, 8. # Log flux amplitude of the outflow at r = 0.
# # Need to check dimming/flux conventions
# tau_flux, 1. # Exponential decay rate of the flux
# biconical_profile_type, both # Type of velocity profile:
# # 'both', 'increase', 'decrease', 'constant'
# biconical_outflow_dispersion, 80. # Dispersion (stddev of gaussian) of biconical outflow, km/s
# # ********************************************************************************
# # VARIABLE BAR FLOW -- in xhat direction along bar in cartesian coordinates,
# # with bar at an angle relative to galaxy major axis (blue)
# # CAUTION!!!
# # variable_bar_flow
# # -------------------
#
# vbar_func_bar_flow, -90.*np.exp(-R/5.) # Bar flow FUNCTION [km/s]. Positive: Outflow. Negative: Inflow.
# phi, 90. # Azimuthal angle of bar [degrees], counter-clockwise from blue major axis.
# # Default is 90 (eg, along galaxy minor axis)
# bar_width, 2 # Width of the bar perpendicular to bar direction.
# # Bar velocity only is nonzero between -bar_width/2 < ygal < bar_width/2.
# # ********************************************************************************
# # AZIMUTHAL PLANAR RADIAL FLOW -- in Rhat direction in cylindrical coordinates
# # (eg, radial in galaxy midplane), with an added azimuthal term
# # CAUTION!!!
# # azimuthal_planar_radial_flow
# # -------------------
#
# vr_func_azimuthal_planar_flow, -90.*np.exp(-R/5.) # Radial flow [km/s].
# # Positive: Outflow. Negative: Inflow.
# m, 2 # Number of modes in the azimuthal pattern. m=0 gives a purely radial profile.
# phi0, 0. # Angle offset relative to the galaxy angle [deg],
# # so the azimuthal variation goes as cos(m(phi_gal - phi0))
# # ********************************************************************************
# # SPIRAL DENSIY WAVE FLOW -- as in Davies et al. 2009, ApJ, 702, 114
# # Here assuming CONSTANT velocity -- try to match real Vrot...
# # CAUTION!!! NO SPACES IN FUNCTION DEFINITONS!
# # spiral_flow
# # -------------------
#
# Vrot_func_spiral_flow, 150.+0.*R # Unperturbed rotation velocity of the galaxy
# dVrot_dR_func_spiral_flow, 0.*R # Derivative of Vrot(R) -- ideally evaluated analytically, otherwise very slow.
# rho0_func_spiral_flow, 1.e11*np.exp(-R/5.) # Unperturbed midplane density profile of the galaxy
# f_func_spiral_flow, (np.sqrt(m**2-2.)*Vrot(R)/cs)*np.log(R) # Function describing the spiral shape, m*phi = f(R)
# # with k = df/dR
# k_func_spiral_flow, (np.sqrt(m**2-2.)*Vrot(R)/cs)/R # Function for radial wavenumber
#
# m, 2 # Number of photometric/density spiral arms.
# cs, 10. # Sound speed of medium, in km/s.
# epsilon, 1. # Density contrast of perturbation (unitless).
# Om_p, 0. # Angular speed of the driving force, Omega_p
# phi0, 0. # Angle offset of the arm winding, in degrees. Default: 0.
# ********************************************************************************
# ********************************************************************************
# ********************************************************************************
# ********************************************************************************
# ZHEIGHT PROFILE
# ---------------
# Initial Values
sigmaz, 0.9 # Gaussian width of the galaxy in z, in kpc
# Tie the zheight to the effective radius of the disk?
# If set to True, make sure sigmaz_fixed is False
zheight_tied, True
# GEOMETRY
# --------
# Initial Values
inc, 62. # Inclination of galaxy, 0=face-on, 90=edge-on
pa, 142.
xshift, 0. # pixels
yshift, 0. # pixels
vel_shift, 0. # km/s
2) Generate Dysmalpy 3D model cube
dysmalpy_make_model.dysmalpy_make_model(param_filename=param_filename,
outdir=outdir, overwrite=True)
------------------------------------------------------------------
Dysmalpy model complete for: GS4_43501
output folder: /Users/jespejo/Dropbox/Postdoc/Data/dysmalpy_test_examples/JUPYTER_OUTPUT_MODEL_WRAPPER/
------------------------------------------------------------------
Examine model cube
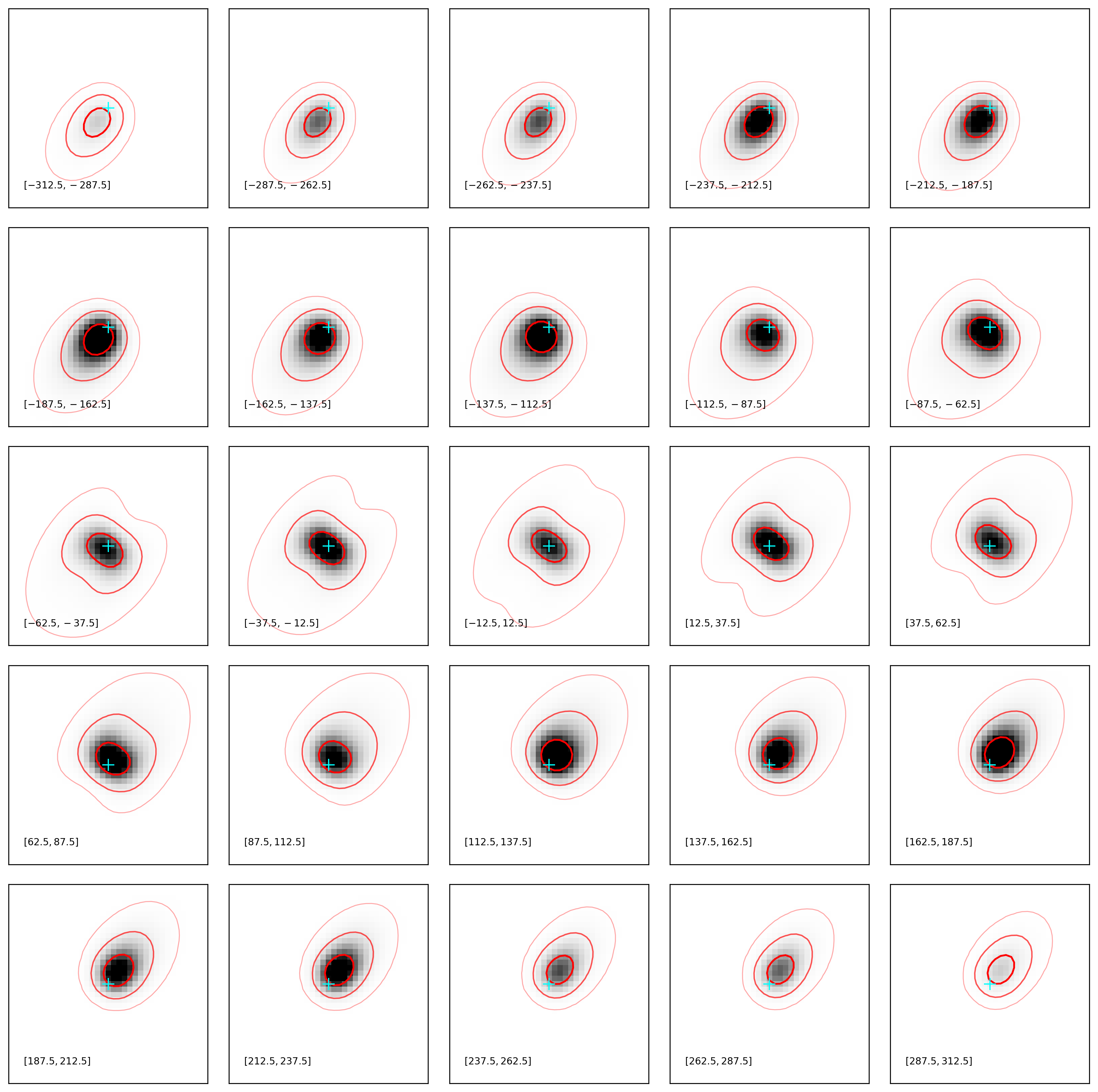
params = utils_io.read_fitting_params(fname=param_filename)
plotting.plot_channel_maps_cube(fname=outdir+params['galID']+'_model_cube.fits',
vbounds = [-312.5, 312.5],delv=25.)
3) Running the model-generation wrapper
Windows
For Windows environments, models are generated by running the make_model_dysmalpy.bat script and selecting the desired parameter file.
Command line usage
To run this script from the command line (e.g, *nix environments), you will need to know the full install path to the DysmalPy fitting wrapper directory.
Additionally, you will need to fully specify all output paths, etc, directly in the parameter file.
The syntax for using this from the command line is as follows:
$ python /PATH/TO/DPY/INSTALL/dysmalpy/fitting_wrappers/dysmalpy_make_model.py make_model_3Dcube.params
(Note also that /PATH/TO/DPY/INSTALL/ must be adjusted for your specific DysmalPy install location.
Finally, the above assumes that the python executable is within your $PATH. If this is not the case, you will need to specify the full path to the pythone executable as well.)
Within python
Finally, this wrapper can be used from within a python session or python script. The usage is exactly as shown in this tutorial (where the wrapper is imported as from dysmalpy.fitting_wrappers import dysmalpy_make_model, and so on).